Hyper Spectral Image Classification¶
Code¶
Introduction¶
Hyperspectral imaging which is also known as imaging spectroscopy, detects radiation of earth surface features in narrow contiguous spectral regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The Airborne Visible Infrared Imaging Spectrometer-Next Generation (AVIRIS-NG) is an airborne hyperspectral sensor of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) with 425 spectral bands ranging from 380 nm to 2510 nm with a bandwidth of 5 nm and spatial resolution of 4-6 m.
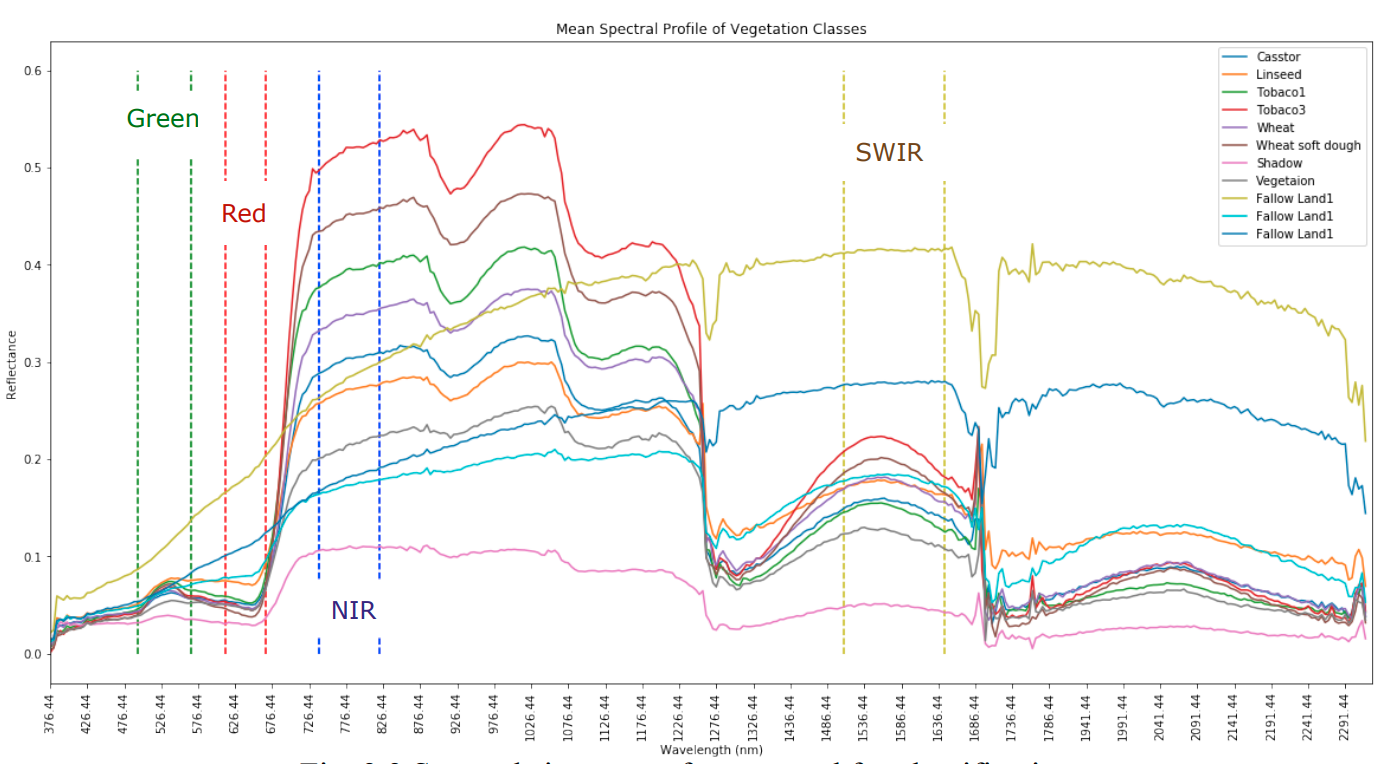
This study aims at pixel-wise identification and discrimination of crop types using AVIRIS-NG hyperspectral images, with novel Parallel Convolutional Neural Networks architecture.
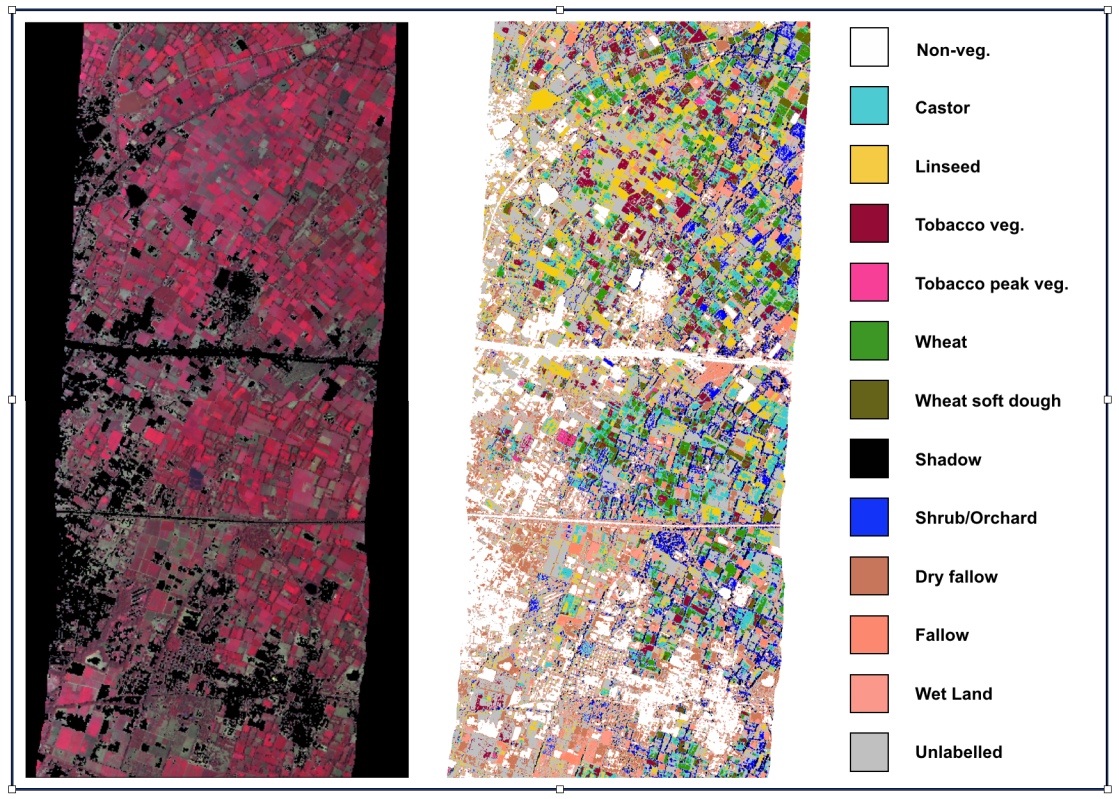
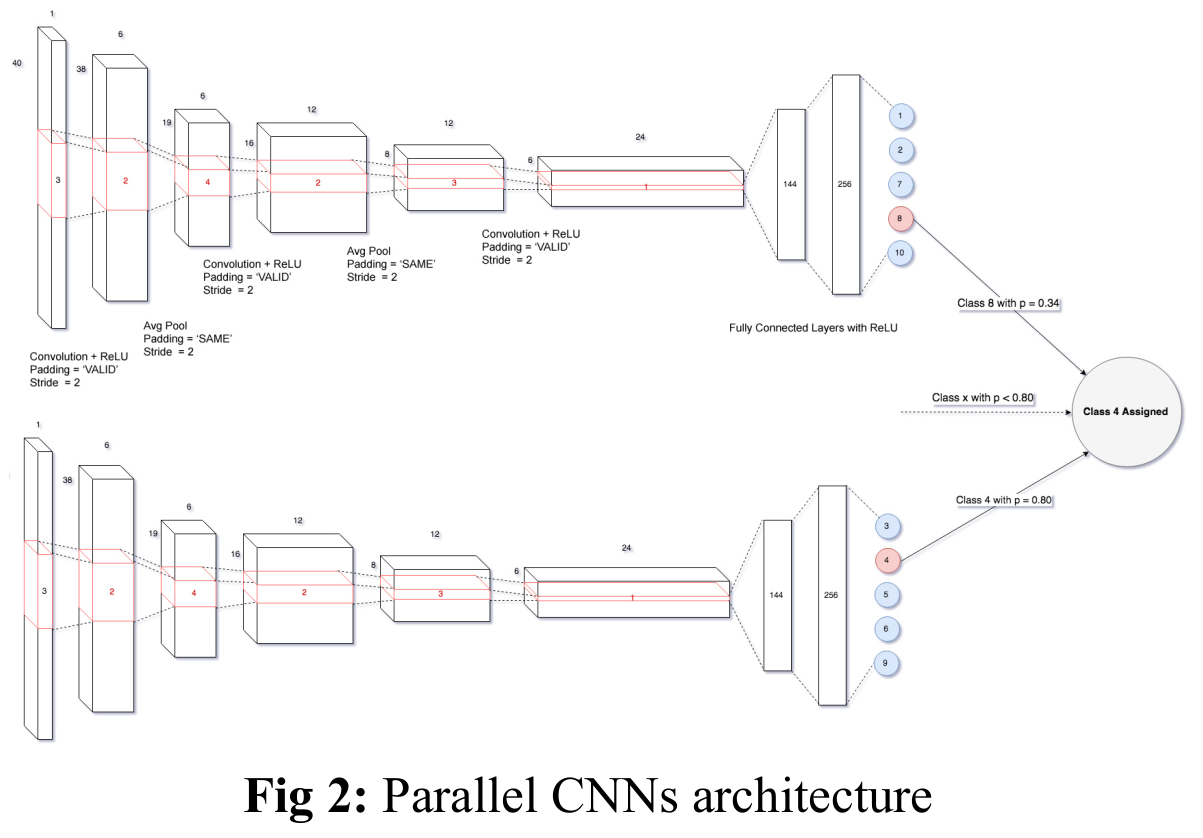
To tackle the challenge posed by a large number of correlated bands, we compare two band selection techniques using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and back traversal of pre-trained Artificial Neural Network (ANN).
-
Bands selected by PCA method
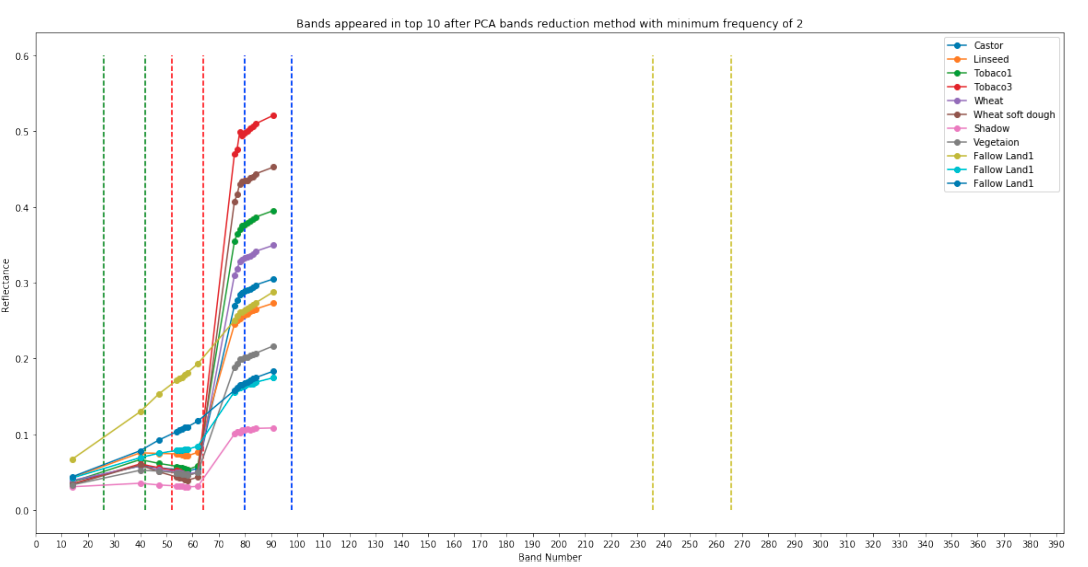
-
Bands selected by ANN method
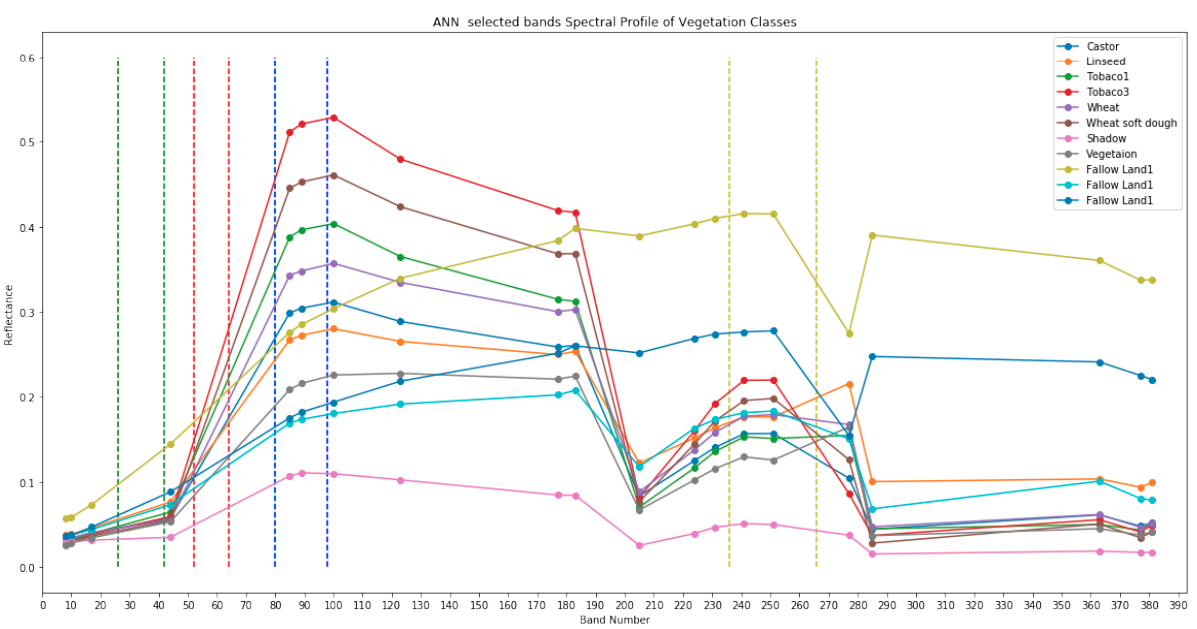
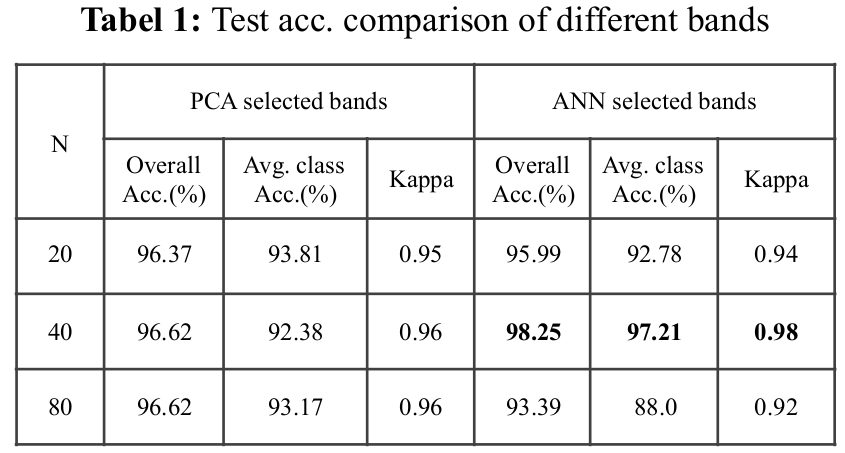
We also propose an automated technique for augmentation of training dataset with a large number of pixels from unlabelled parts of an image, based on Euclidian distance. Experiments show that bands selected by ANN achieve higher accuracy compare to PCA selected bands with automated data augmentation.
Paper¶
@INPROCEEDINGS{8897897,
author={Patel, Hetul and Bhagia, Nita and Vyas, Tarjni and Bhattacharya, Bimal and Dave, Kinjal},
booktitle={IGARSS 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium},
title={Crop Identification and Discrimination Using AVIRIS-NG Hyperspectral Data Based on Deep Learning Techniques},
year={2019},
volume={},
number={},
pages={3728-3731},
doi={10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8897897}}